Worms Indicate Soil Health
The Earth worm – a garden partner that gets ‘no respect’. As I was digging weeds and dividing perennials this weekend I gently returned the worms back to the soil. I also noticed little mounds of soil in the lawn and pine needles standing on end in the beds.


The mighty worm did this! Some species of worms stay close to the surface of the soil. They are the Epigeic species. They are small worms that are not harmed when soil temperatures rise and moisture levels lessen. The Epigeic worms are commonly found in the compost pile. The Endogeic species stay in the upper levels of soil, where their tunnels are more temporary. The tunnels fill up with casts (poop) as they eat through the soil and deposit it as castings. The deep burrowing species, the Anecic species are commonly know as night-crawlers, and they burrow vertically, sometimes as deep as 8 feet into the ground. The night-crawlers are the guys that leave the mound of debris at the mouth of the borrow.

Earth Worms have both male and female parts which is known as hermaphrodites. Worms mate throughout the year.

After mating each worm constructs a cocoon and within a couple of weeks new worms are hatched. The cocoons are only about 1/4”, and if I have seen one, I didn’t know it. I’ll keep a watch out now!
The earthworms enhance the soil in four ways.
1) The enhance soil structure.

Pores in the soil hold air, and water - The basics for plant growth. If the pores are too small, oxygen cannot get to roots of plants. If the pores are too large, water drains away from roots too quickly.
2) Worms enhance microorganism activity in soil. As worms eat microorganisms, such as fungi, bacteria, protozoa and nematodes, the castings they leave are even more filled with active microorganisms. As the worms digest their food, they produce castings that are already digested nutrients, which makes the nutrients readily available to plants. Other microorganisms deposited in the poop, create enzymes that plants also use to convert nutrients.

3) Earthworms mix the soil. They push up the nutrient rich casting that give texture to the soil. They also draw down into the soil, debris that will decompose, feed the microorganisms, and create usable nutrients for plants. It is estimated that worms turn over of the top six inches of soil every ten to twenty years.
4) Earthworms increase water filtration by improving the porosity. This can reduce runoff and decrease pollution that drains into our watershed.
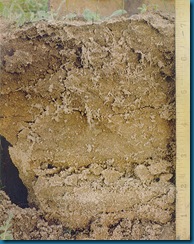

This picture shows the lack of organic material in the pale, dense soil. Note the roots are barely penetrating the surface. The second picture is one year after organic matter has been added. The soil is darker, roots extend deep into the soil. Microorganisms get active when the organic matter, such as beneficial worm castings, is available. Worms generate tons of casting per acre, per year, dramatically changing the soil structure.
Worm manure or casting is rich in nutrients. Nitrogen, Phosphorous, and Potassium, as well as Magnesium are readily available to plants. The casting create a home for microorganisms, and provide a base for water to be absorbed and held in the soil.

Few predators bother the earthworm. We know that birds feed on earthworms, but so do turtles and toads. Moles in the lawn or garden usually indicate a high population of worms also.



As worms enhance the soil from below, we can also add worm casting


Making a ‘tea’ with worm casting is another way to water and feed plants. Soak worm casting

Vermiculture, the cultivating of worms and worm castings, is another source of beneficial nutrients for the lawn and garden. I will explain this practice at another time.
Using chemical herbicides and pesticides on the soil can harm the life beneath the surface. Chemicals will damage the balance of nature and could take years to restore that balance.

Organic matter in any form is good for the soil. The garden debris can turn your soil into an active bio culture teeming with microorganisms and worms.
If you build it (good soil), they (worms) will come. Have you used worm castings? What was your experience?
Thanks for stopping by today.
.
I've never used worm castings, but this was great information. When digging, I always look for worms - and when i find them, I silently rejoice!
ReplyDeleteGreat post. Thanks for sharing all the information. Your photos were particularly good.
ReplyDeleteGreat info on worms. I've been finding a lot of them digging in the garden this spring. Worms are always a happy find.
ReplyDeleteI know I've got good soil when I see worms in it. It's the best sign of a good soil. Plus, if you want to take up fishing, you can harvest your own bait!
ReplyDeleteGreat post Claudia, I have used both, worm castings and worm juice. Killed a couple of plants because applied too much worm juice and it is very strong. I used to put 1/3 worm juice and fill watering 9 litre watering can with 2/3 water.
ReplyDelete